Mid Ureteric Transitional Cell Carcinoma
Submitted by Stephen Moore (Sonographer), Greater Glasgow and Clyde NHS Scotland
Patient Presentation/ Clinical information:
A 63 year old female patient presented for a renal ultrasound following a recent computed tomography (CT) chest highlighted right sided hydronephrosis. The CT was undertaken due to a history of shortness of breath (SOB), smoking and weight loss. The patient has a previous medical history of chronic atelectasis, however no history of malignancy or further history of note.
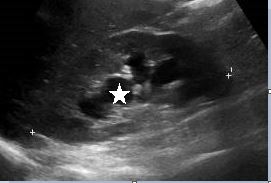
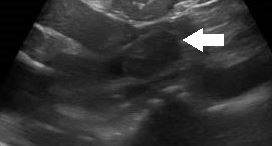
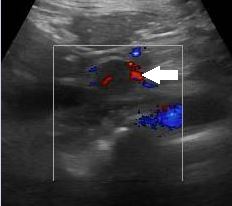
B-mode ultrasound demonstrated moderate right sided hydronephrosis with preservation of the renal cortex (fig1). However, there was dilation of the proximal half of the right ureter which could be traced to the mid ureteric region. At this level there was a small degree of mural thickening, furthermore there was a 24 x 12 mm solid lesion seen extending from the ureteric wall into the ureteric lumen (fig 2). On colour Doppler interrogation there was evidence of increased vascularity within this lesion (fig 3). These findings raised concern for an invasive intraluminal neoplasm. Given these findings and the clinical history, urgent cross sectional imaging and clinical review by the urology team was conducted. The left kidney and urinary bladder were unremarkable on ultrasound.
Computed Tomography (CT) imaging was undertaken on a two week wait pathway and confirmed the ultrasound findings of a moderate right-sided hydronephrosis and proximal hydroureter, which terminated in an abrupt transition at the level of the mid ureter where an enhancing soft tissue mass was seen. CT concluded that these findings were suspicious for ureteric TCC and suggested direct visualisation (fig 4). The patient then went on to have a cystoscopy which confirmed these findings.
Images/ Videos:
Figure 1: Right sided hydronephrosis with renal cortical thinning (Star: Hydronephrosis)
Figure 2: Mural thickening and intraluminal lesion (Arrow: TCC)
Figure 3: Colour Doppler interrogation of the lesion showing increased vascularity (Arrow: TCC)
Figure 4: Coronal Sagittal oblique CT of the TCC within the ureter (Arrow: TCC. Star: Hydronephrosis)